There is a paradox on the coronary coronary heart of our altering native climate. Whereas the blanket of air close to the Earth’s flooring is warming, lots of the surroundings above is becoming dramatically colder. The similar gases which is perhaps warming the underside few miles of air are cooling the quite a bit larger expanses above that stretch to the sting of home.
This paradox has prolonged been predicted by native climate modelers, nonetheless solely simply recently quantified intimately by satellite tv for pc television for laptop sensors. The model new findings are providing a definitive affirmation on one important topic, nonetheless on the similar time elevating completely different questions.
The good news for native climate scientists is that the information on cooling aloft do better than affirm the accuracy of the fashions that decide flooring warming as human-made. A model new look at printed this month throughout the journal PNAS by veteran native climate modeler Ben Santer of the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution found that it elevated the facility of the “signal” of the human fingerprint of native climate change fivefold, by lowering the interference “noise” from background pure variability. Sander says the discovering is “incontrovertible.”
Nevertheless the model new discoveries regarding the scale of cooling aloft are leaving atmospheric physicists with new worries — regarding the safety of orbiting satellites, regarding the future of the ozone layer, and regarding the potential of these quick changes aloft to go to sudden and unanticipated turmoil on our local weather beneath.
Will enhance in CO2 are literally “manifest all by way of your total perceptible surroundings,” a physicist says.
Until simply recently, scientists often called the distant zones of the upper surroundings the “ignorosphere” because of they knew so little about them. So now that they know additional, what are we learning, and will it reassure or alarm us?
The Earth’s surroundings has quite a lot of layers. The world everyone knows biggest, because of it is the place our local weather happens, is the troposphere. This dense blanket of air 5 to 9 miles thick accommodates 80 p.c of the mass of the surroundings nonetheless solely a small fraction of its amount. Above it are giant open areas of progressively a lot much less dense air. The stratosphere, which ends spherical 30 miles up, is adopted by the mesosphere, which extends to 50 miles, after which the thermosphere, which reaches better than 400 miles up.
From beneath, these distant zones appear as placid and pristine blue sky. Nevertheless in fact, they’re buffeted by extreme winds and enormous tides of rising and descending air that typically invade our troposphere. And the precedence is that this already dynamic setting might change as soon as extra because it’s infiltrated by CO2 and completely different human-made chemical compounds that mess with the temperature, density, and chemistry of the air aloft.
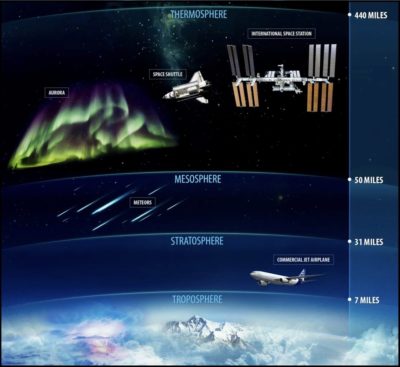
Earth’s atmospheric layers.
NOAA / Yale Environment 360
Native climate change is type of always considered with regards to the underside areas of the surroundings. Nevertheless physicists now warn that we now have to rethink this assumption. Will enhance throughout the amount of CO2 are literally “manifest all by way of your total perceptible surroundings,” says Martin Mlynczak, an atmospheric physicist on the NASA Langley Evaluation Coronary heart in Hampton, Virginia. They’re “driving dramatic changes [that] scientists are merely now beginning to perceive.” These changes throughout the wild blue yonder far above our heads might feed once more to change our world beneath.
The story of adjusting temperatures throughout the surroundings the least bit ranges is principally the story of CO2. Everyone knows all too successfully that our emissions of better than 40 billion tons of the gasoline yearly are warming the troposphere. This happens because of the gasoline absorbs and re-emits photograph voltaic radiation, heating completely different molecules throughout the dense air and elevating temperatures normal.
Nevertheless the gasoline does not all hold throughout the troposphere. It moreover spreads upward through your total surroundings. We now know that the pace of improve in its give attention to the excessive of the surroundings is as good as on the bottom. Nevertheless its influence on temperature aloft could also be very fully completely different. Throughout the thinner air aloft, lots of the heat re-emitted by the CO2 does not bump into completely different molecules. It escapes to accommodate. Blended with the upper trapping of heat at lower ranges, the result is a quick cooling of the encircling surroundings.
The cooling of the upper air moreover causes it to contract, which points NASA. The sky is falling — really.
Satellite tv for pc television for laptop data have simply recently revealed that between 2002 and 2019, the mesosphere and reduce thermosphere cooled by 3.1 ranges F (1.7 ranges C ). Mlynczak estimates that the doubling of CO2 ranges thought seemingly by later this century will set off a cooling in these zones of spherical 13.5 ranges F (7.5 ranges C), which is between two and thrice ahead of the widespread warming anticipated at flooring stage.
Early native climate modelers predicted once more throughout the Sixties that this combination of tropospheric warming and strong cooling elevated up was the seemingly influence of accelerating CO2 throughout the air. Nevertheless its present detailed affirmation by satellite tv for pc television for laptop measurements tremendously enhances our confidence throughout the have an effect on of CO2 on atmospheric temperatures, says Santer, who has been modeling native climate change for 30 years.
This month, he used new data on cooling throughout the heart and better stratosphere to recalculate the facility of the statistical “signal” of the human fingerprint in native climate change. He found that it was tremendously strengthened, particularly because of the additional revenue equipped by the lower stage of background “noise” throughout the larger surroundings from pure temperature variability.
Santer found that the signal-to noise ratio for human have an effect on grew fivefold, providing “incontrovertible proof of human outcomes of the thermal building of the Earth’s surroundings.” We’re “principally altering” that thermal building, he says. “These outcomes make me very fearful.”

A view of the home shuttle Endeavor exhibiting quite a few layers of the surroundings — the mesosphere (blue), the stratosphere (white), and the troposphere (orange).
NASA
A whole lot of the evaluation analyzing changes aloft has been carried out by scientists employed by NASA. The home firm has the satellites to measure what is going on, but it surely certainly moreover has a particular curiosity throughout the implications for the safety of the satellites themselves.
This curiosity arises because of the cooling of the upper air moreover causes it to contract. The sky is falling — really.
The depth of the stratosphere has diminished by about 1 p.c, or 1,300 ft, since 1980, in step with an analysis of NASA data by Petr Pisoft, an atmospheric physicist at Charles Faculty in Prague. Above the stratosphere, Mlynczak found that the mesosphere and reduce thermosphere contracted by practically 4,400 ft between 2002 and 2019. Part of this shrinking was ensuing from a short-term decline in photograph voltaic train that has since ended, nonetheless 1,120 ft of it was ensuing from cooling attributable to the extra CO2, he calculates.
This contraction means the upper surroundings is becoming a lot much less dense, which in flip reduces drag on satellites and completely different objects in low orbit — by spherical a third by 2070, calculates Ingrid Cnossen, a evaluation fellow on the British Antarctic Survey.
On the face of it, that is good news for satellite tv for pc television for laptop operators. Their payloads must hold operational for longer sooner than falling once more to Earth. Nevertheless the difficulty is the alternative objects that share these altitudes. The rising amount of home junk — bits of package of varied varieties left behind in orbit — are moreover sticking spherical longer, rising the hazard of collisions with presently operational satellites.
In 2020, the Arctic had its first full-blown ozone hole, with better than half the ozone layer misplaced in places.
Better than 5000 energetic and defunct satellites, along with the Worldwide Home Station, are in orbit at these altitudes, accompanied by better than 30,000 recognized objects of particles better than 4 inches in diameter. The hazards of collision, says Cnossen, will develop ever larger as a result of the cooling and contraction gathers tempo.
This may be harmful for enterprise at home corporations, nonetheless how will the changes aloft affect our world beneath?
One enormous concern is the already fragile state of the ozone layer throughout the lower stratosphere, which protects us from harmful photograph voltaic radiation that causes pores and pores and skin cancers. For lots of the 20th century, the ozone layer thinned beneath assault from industrial emissions of ozone-eating chemical compounds much like chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs). Outright ozone holes normal each spring over Antarctica.
The 1987 Montreal Protocol aimed to heal the annual holes by eliminating these emissions. Nevertheless it is now clear that one different challenge is undermining this effort: stratospheric cooling.
Ozone destruction operates in overdrive in polar stratospheric clouds, which solely sort at very low temperatures, considerably over polar areas in winter. Nevertheless the cooler stratosphere has meant additional occasions when such clouds can sort. Whereas the ozone layer over the Antarctic is slowly reforming as CFCs disappear, the Arctic is proving fully completely different, says Peter von der Gathen of the Alfred Wegener Institute for Polar and Marine Evaluation in Potsdam, Germany. Throughout the Arctic, the cooling is worsening ozone loss. Von der Gathen says the rationale for this distinction should not be clear.
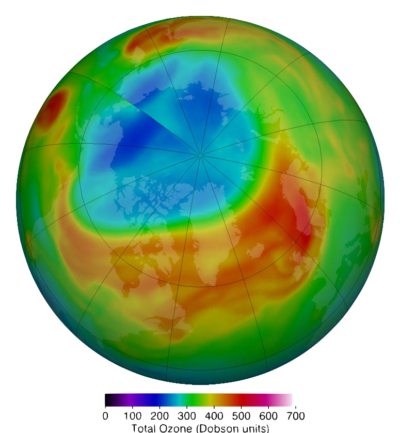
Map exhibiting ozone hole over the Arctic in March 2020.
NASA
Throughout the spring of 2020, the Arctic had its first full-blown ozone hole with better than half the ozone layer misplaced in places, which von der Gathen blames on rising CO2 concentrations. It might probably be the first of many. In a present paper in Nature Communications, he warned that the continued cooling means current expectations that the ozone layer must be completely healed by mid-century are practically really overly optimistic. On current traits, he acknowledged, “circumstances favorable for big seasonal lack of Arctic column ozone might persist and even worsen until the highest of this century … for for much longer than is usually appreciated.”
That’s made additional relating to because of, whereas the areas beneath earlier Antarctic holes have been largely devoid of people, the areas beneath future Arctic ozone holes are doubtlessly quite a few the additional densely populated on the planet, along with Central and Western Europe. If we thought the thinning ozone layer was a 20th century worry, we would should suppose as soon as extra.
Chemistry should not be the one topic. Atmospheric physicists are moreover rising concerned that cooling might change air actions aloft in methods wherein impinge on local weather and native climate at flooring stage. One of many turbulent of these phenomena is called sudden stratospheric warming. Westerly winds throughout the stratosphere periodically reverse, main to large temperatures swings all through which components of the stratosphere can warmth by as quite a bit as 90 ranges F (50 ranges C) in a number of days.
That’s normally accompanied by a quick sinking of air that pushes onto the Atlantic jet stream on the excessive of the troposphere. The jet stream, which drives local weather strategies extensively all through the Northern Hemisphere, begins to snake. This disturbance might trigger a variety of extreme local weather, from persistent intense rains to summer season droughts and “blocking highs” which will set off weeks of intense chilly winter local weather from jap North America to Europe and components of Asia.
This quite a bit is already recognized. Before now 20 years, local weather forecasters have included such stratospheric influences of their fashions. This has significantly improved the accuracy of their long-range forecasts, in step with the Met Office, a U.Okay. authorities forecasting firm.
“If we don’t get our fashions correct about what is going on up there, we might get points improper down beneath.”
The question now being requested is how the extra CO2 and normal stratospheric cooling will have an effect on the frequency and depth of these sudden warming events. Mark Baldwin, an area climate scientist on the Faculty of Exeter in England, who has studied the phenomenon, says most fashions agree that sudden stratospheric warming is actually delicate to additional CO2. Nevertheless whereas some fashions predict many additional sudden warming events, others suggest fewer. If we knew additional, Baldwin says, it might “lead to improved confidence in every long-term local weather forecasts and native climate change projections.”
It is becoming ever clearer that, as Gary Thomas, an atmospheric physicist on the Faculty of Colorado Boulder, locations it, “If we don’t get our fashions correct about what is going on up there, we might get points improper down beneath.” Nevertheless bettering fashions of how the upper surroundings works — and verifying their accuracy — requires good up-to-date data on precise circumstances aloft. And the provision of that data is about to dry up, Mlynczak warns.
A whole lot of the satellites which have outfitted information from the upper surroundings over the earlier three a few years — delivering his and others’ forecasts of cooling and contraction — are reaching the ends of their lives. Of six NASA satellites on the case, one failed in December, one different was decommissioned in March, and three additional are set to shut down rapidly. “There’s as however no new mission deliberate or in enchancment,” he says.
Mlynczak is hoping to reboot curiosity in monitoring with a selected session that he is organizing on the American Geophysical Union this fall to debate the upper surroundings as “the next frontier in native climate change.” With out continued monitoring, the concern is we might rapidly be returning to the occasions of the ignorosphere.
